Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health have collected and digitized all weekly surveillance reports for reportable diseases in the United States going back more than 125 years. The digitized dataset is dubbed Project Tycho™, for 16th century Danish nobleman Brahe, whose meticulous astronomical observations enabled Johannes Kepler to derive the laws of planetary motion.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health have collected and digitized all weekly surveillance reports for reportable diseases in the United States going back more than 125 years. The digitized dataset is dubbed Project Tycho™, for 16th century Danish nobleman Brahe, whose meticulous astronomical observations enabled Johannes Kepler to derive the laws of planetary motion.
“Brahe’s data were essential to Kepler’s discovery of the laws of planetary motion,” said senior author Donald S. Burke, MD, Pitt Public Health dean and UPMC-Jonas Salk Chair of Global Health. “Similarly, we hope that our Project Tycho™ disease database will help spur new, life-saving research on patterns of epidemic infectious disease and the effects of vaccines. Open access to disease surveillance records should be standard practice, and we are working to establish this as the norm worldwide.”
The easily searchable database is free and publicly available on the Project Tycho™ Web site. Supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the project’s goal is to aid scientists and public health officials in the eradication of deadly and devastating diseases.
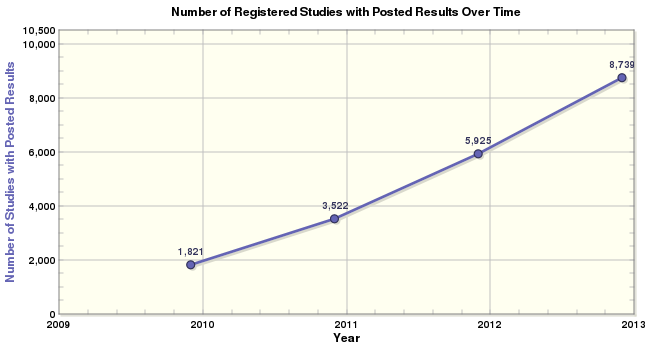
The researchers obtained all weekly notifiable disease surveillance tables published between 1888 and 2013—approximately 6,500 tables—in various historical reports, including the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. These tables were available only in paper format or as PDF scans in online repositories that could not be read by computers and had to be hand-entered. With an estimated 200 million keystrokes, the data—including death counts, reporting locations, time periods and diseases—were digitized. A total of 56 diseases were reported for at least some period of time during the 125-year time span, with no single disease reported continuously.
“Historical records are a precious yet undervalued resource. As Danish philosopher Soren Kierkegaard said, we live forward but understand backward,” explained Dr. Burke. “By ‘rescuing’ these historical disease data and combining them into a single, open-access, computable system, we now can better understand the devastating impact of epidemic diseases, and the remarkable value of vaccines in preventing illness and death.”
*Parts of this article were reprinted from Pitt Unlocks Trove of Public Health Data to Help Fight Deadly Contagious Diseases, Pitt Public Health, In the News, 11/27/2013.
See also: W.G. van Panhuis, J. Grefenstette, S.Y. Jung, N.S. Chok, A. Cross, H. Eng, B.Y. Lee, V. Zadorozhny, S. Brown, D. Cummings, D.S. Burke, “Contagious Diseases in the United States from 1888 to the Present,” New England Journal of Medicine, 369(22): 2152-8, November 28, 2013.
This research was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Grant 49276 and NIH grant U54GM088491.
~Nancy Tannery


 The First Consult App provides access to evidence-based medical information at the point-of-care without an Internet connection. Data is stored on your mobile device, so access is instantaneous. The app is available to Pitt and UPMC users through the HSLS subscription to the
The First Consult App provides access to evidence-based medical information at the point-of-care without an Internet connection. Data is stored on your mobile device, so access is instantaneous. The app is available to Pitt and UPMC users through the HSLS subscription to the