When you need several articles fast, and you are not concerned with identifying every article on the topic, the following tools and techniques are just what the doctor ordered!
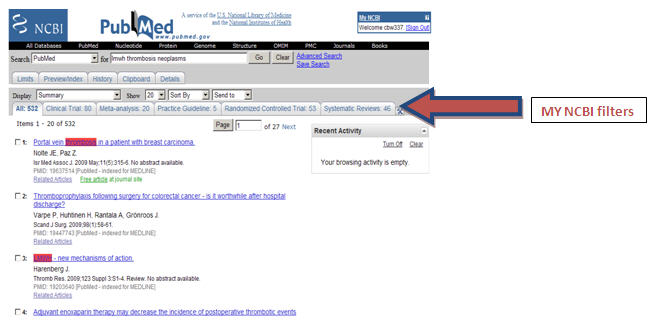
- Get your own PubMed MY NCBI account and set up your own search filters. For instance, I frequently search for evidence-based studies. MY NCBI search filters include: clinical trials, meta-analysis, practice guidelines, and systematic reviews. Your filters could be set to any number of subject areas including: nursing, AIDS, cancer, or bioethics. If you are a pediatrician or geriatrician, you can set your search filters to quickly locate articles on children or the aged.
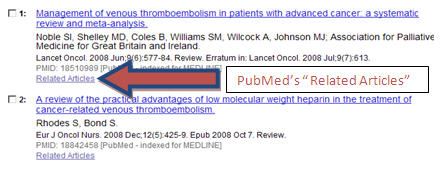
- When you locate an article of particular interest in PubMed, don’t forget to use the Related Articles link. The Related Articles link is a quick way to find similar articles to your article of interest. This feature retrieves PubMed citations that are closely related to the article using word-weighted calculations and algorithms. The related articles will be displayed in ranked order from most to least relevant, with the “linked from” citation (your original article) displayed first.
- Google Scholar is a quick way to find that hidden article. Google has arrangements with scholarly publishers to query their servers and to take the words from their electronic articles and add them to the Google database. This gives you the opportunity to search the content of the entire article. Google Scholar displays the results using the number of times the article was cited in the Google database as a marker of its page rank or relevancy score.
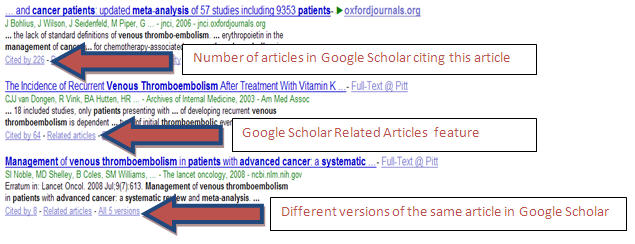
When you find that Google Scholar gem, use Google Scholar’s Related articles link to locate similar articles.
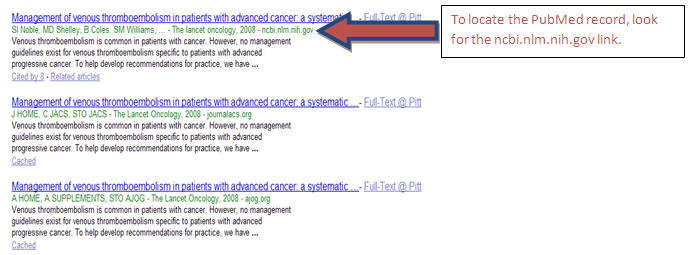
Google Scholar gets it content from many sources, so there can be more than one version of the same article in Google Scholar. To locate the PubMed abstract for an article, click on All # versions link. The PubMed record version will have PubMed’s URL “ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.”
For a more detailed comparison of Google Scholar vs. PubMed, see “Google Scholar vs. PubMed for Health Sciences Literature Searching” in this issue.
Look for “Quick Searching Tools & Techniques, Part 2,” in the December issue of the HSLS Update. For help with these search tips and techniques, contact your Liaison Librarian or Ask A Librarian.
~ Charles Wessel