The answer is simple and yet complex.
The answer is simple and yet complex.
From mid-November to mid-December, the National Library of Medicine (NLM) does year-end-processing. During this time, extensive maintenance is done on MEDLINE. MEDLINE is the NLM database of biomedical journal citations and is the primary component of PubMed.
Daily “routine maintenance” on MEDLINE happens throughout the year and includes a variety of edits to MEDLINE citations. These edits include corrections of misspellings; the addition of published errata, retractions, and comments (including author replies); changes to journal titles and their abbreviations; changes to supplementary concepts such as chemicals, protocols, and diseases; and adjustments to MeSH (Medical Subject Headings).
The primary purpose of year-end maintenance is to update MeSH. Each year, new MeSH headings are added, other headings are replaced with more up-to-date terminology, and out-dated headings are deleted with no replacement. From mid-November to mid-December, NLM applies these MeSH heading changes to MEDLINE citations where necessary.
Things you should know when searching PubMed during the year-end-processing period:
- All regular routine corrections to MEDLINE are on hold. MEDLINE corrections will appear when the update is complete.
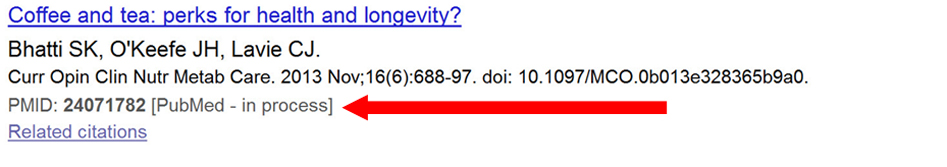
- “In process” citations (Figure 1) will continue to be added to PubMed. In-process citations do not have medical subject headings assigned to them, but they have undergone quality control review. As a result, the number of PubMed records labeled “in process” will temporarily increase, and the number of MEDLINE records will stay the same.
- If you use a PubMed filter (human, review, etc.) or a MeSH heading in a search, you may not see any new MEDLINE citations until year-end-processing is complete in mid-December.
Things you should know when searching PubMed after the year-end-processing period:
- By mid-December when year-end-processing is complete, “in process” MEDLINE citations will have 2014 medical subject headings assigned to them and these citations are then noted in PubMed as “indexed for MEDLINE” (Figure 2). Searches, including, “My NCBI” stored searches, containing these MeSH headings will automatically retrieve all applicable MEDLINE records.
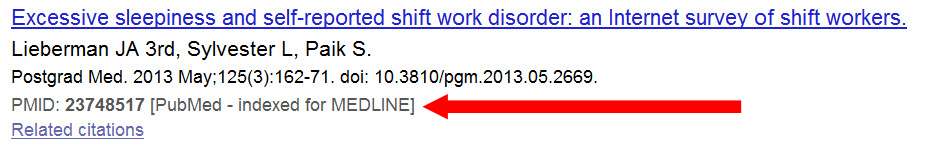
Figure 2
- You can scan the 2014 New MeSH descriptors to identify the MeSH headings that apply to your clinical and research interests.
- At the same time, take a look at:
- Changed Descriptors—2014 and Deleted Descriptors— 2014.
- New Descriptors by Tree Subcategory—2014 allows you to identify new 2014 MeSH headings within broad subject categories.
- You may want to check your saved My NCBI searches to make sure they reflect the 2014 MeSH headings.
For more information, send an e-mail to Ask a Librarian or call the HSLS Main Desk at 412-648-8866.
~ Charlie Wessel